1. About the CEO Report
In the CEO reports, Ilia Management Consulting Company aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of organizational performance, economic and business conditions, and forecasts for the coming year by examining the concerns, approaches, lifestyles, and work styles of Iranian CEOs.
The main difference between this issue, published in 1404, and the previous issue is the addition of several new sections to the report and the use of more diverse statistical methods to analyze the correlation of parameters and the significance between them.
In short, the main focus of the managers in this issue of the report is on financial and liquidity issues, and their responses show a lot of effort to navigate through complex and ambiguous situations. For this reason, using the symbol “fog” which represents ambiguity and the symbol “marathon” which represents perseverance and long-term effort in difficult conditions, the title “Marathon in the Fog” has been chosen for the CEOs’ report in the fourth issue.
It is worth noting Full text of the report It includes more details on each of the items mentioned, as well as items such as sample information, research methodology, etc., for those interested in studying. Below, we will review some of the most important results of this report.
2. CEOs and macro issues
Economic prosperity, organizational performance, and CEO optimism:
- 46% of CEOs participating in the current survey predicted a major recession for 1404. 35% of managers believe that the Iranian economy will witness a relative recession in 1404. According to Latest PwC report Regarding CEOs’ predictions about the global economic environment, 58% of CEOs are optimistic about global economic prosperity in 2025.
- 81% of CEOs are not optimistic about Iran’s economic prosperity in 1404.
- Only 12% of CEOs are optimistic about Iran’s economic prosperity in 1404, which is the same as in 1403.
- The predictions of CEOs of different industries regarding Iran’s economic situation in 1404 (2025) have been different, with CEOs active in the fields of paper, printing and reproduction, as well as pharmaceutical and health care, being the most optimistic, and CEOs of the civil engineering and construction industries, as well as water and waste management, being the most pessimistic about economic prosperity in 1404 (2025).
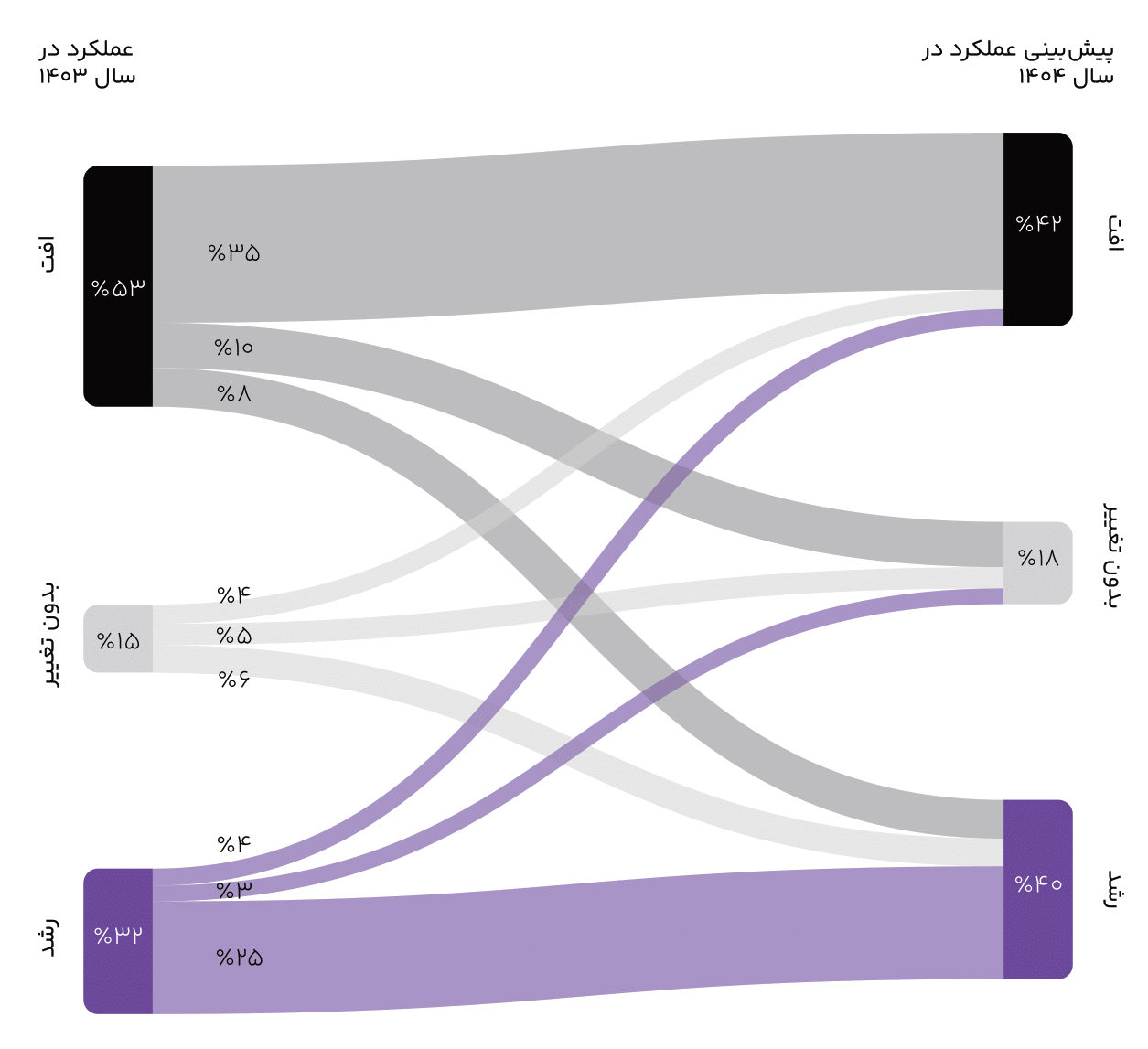
- While last year 63% of CEOs hoped for growth in their organization’s financial performance, this figure has decreased to 40% for 1404. Thus, optimism regarding growth in financial performance has decreased by 23% compared to the previous year, which shows a significant decline in this area.
- Also, managers’ pessimism regarding their organization’s future financial performance has increased by 17 percentage points, and 18% of CEOs do not anticipate any change in their organization’s financial performance in 1404.
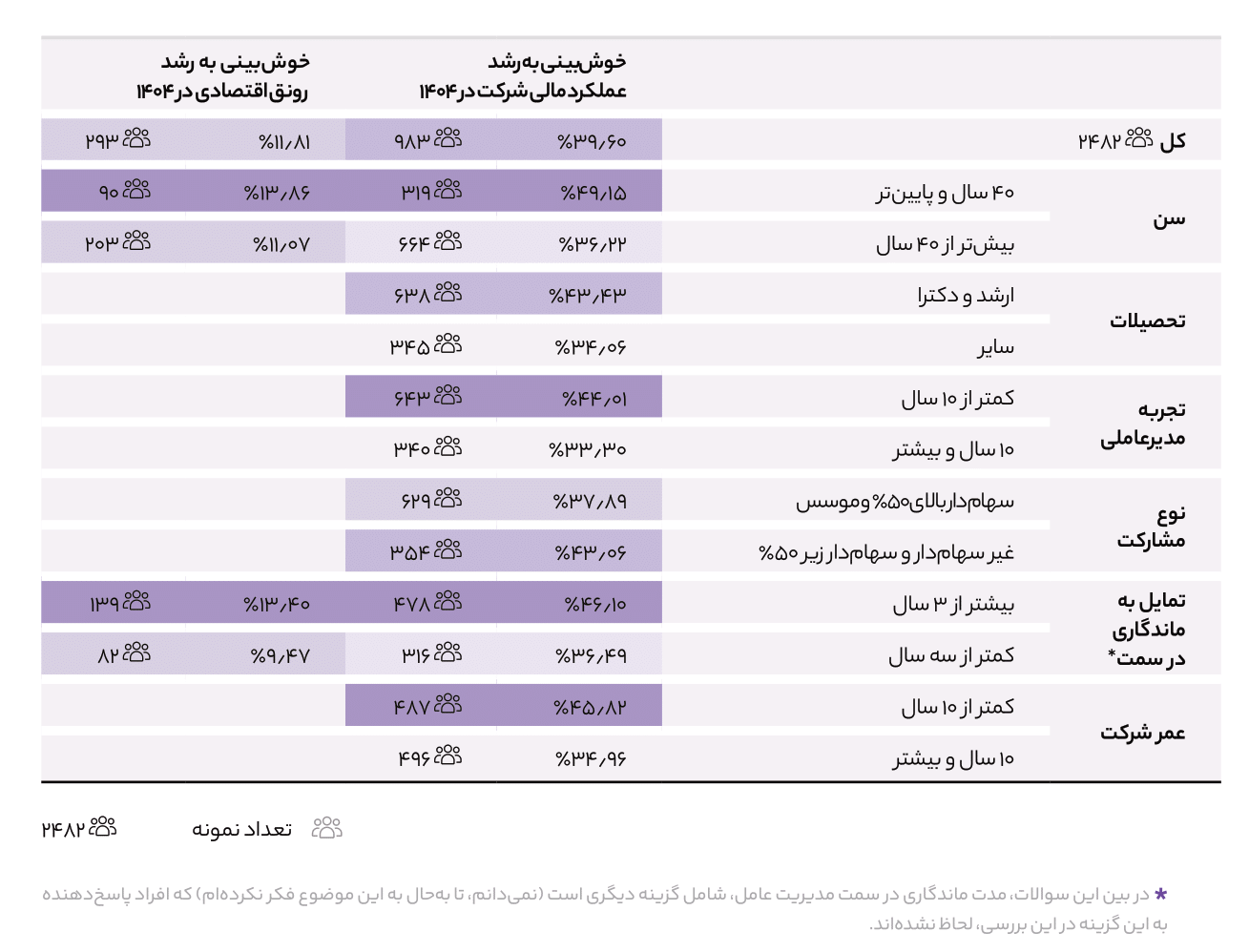
Correlation between economic status and financial performance:
- Based on the analysis conducted (correlation test for two parameters), there is a direct correlation between optimism about the country’s economic prosperity and the organization’s future performance; meaning that as optimism about economic prosperity increases or decreases, optimism about the organization’s performance in 1404 also increases or decreases.
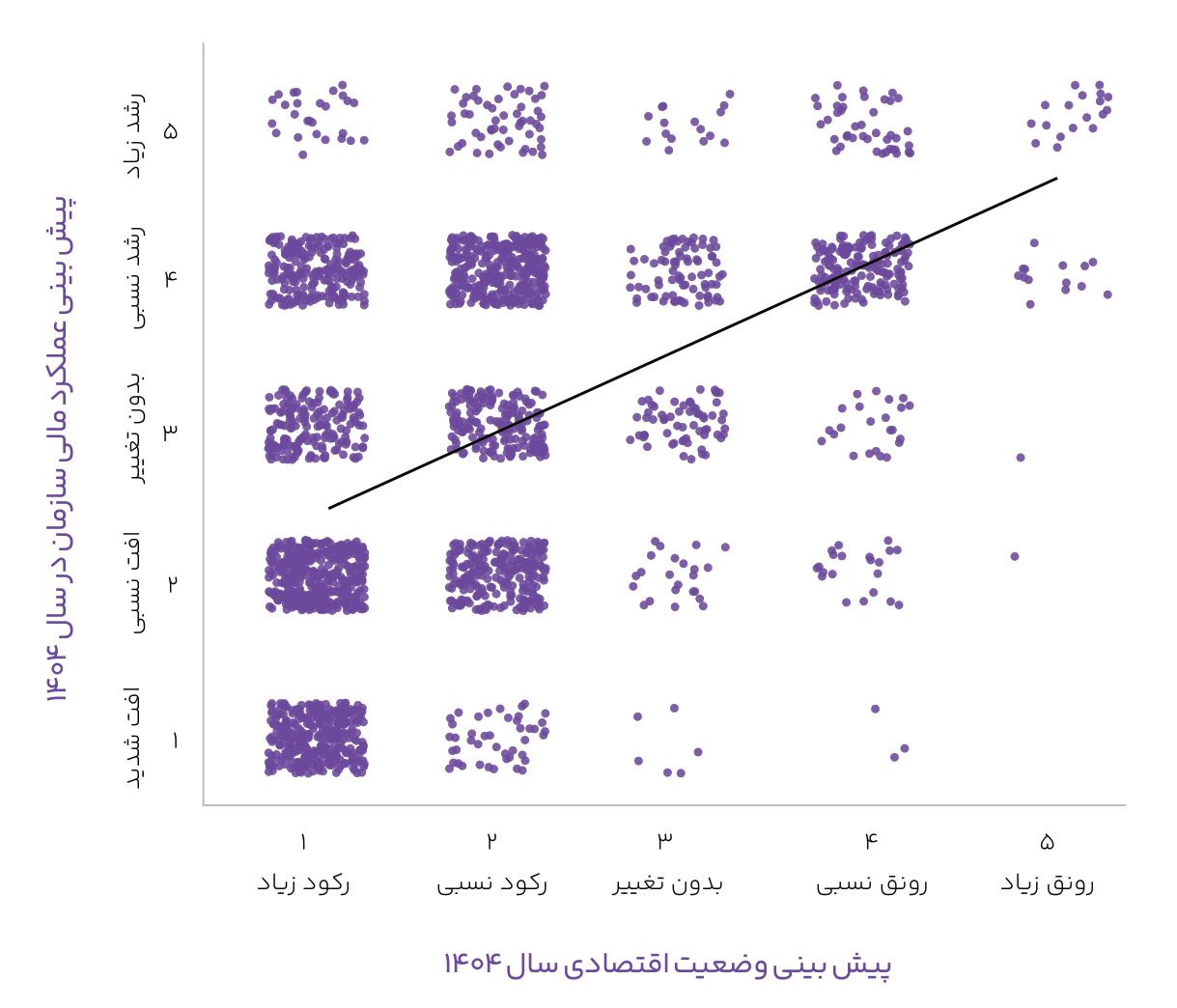
Achieving financial and non-financial goals:
- Comparing the companies’ financial performance with their performance forecasts for 1403 shows that CEOs experienced 31 percentage points less growth than predicted and also experienced 28 percentage points more decline in performance than predicted.
- The results of the analysis show that 44% of participating CEOs made little progress in achieving their organization’s non-financial goals (in areas such as infrastructure development, new investment, restructuring, etc.) in 1403. It should be noted that 40% of CEOs achieved a moderate level of their non-financial goals in 1403.
- Based on the analysis, there is a direct correlation between the achievement of non-financial goals in 1403 and the organization’s financial performance this year; meaning that with the growth or decline in the financial performance of the previous year, the achievement of non-financial goals also grows or declines.
Shadow of doubt over government actions and the role of the private sector in improving conditions:
- 83% of CEOs are not optimistic about the positive impact of government actions on improving business conditions. 29% of CEOs believe that the current government actions will not have an impact on the current trend of the country, another 54% are pessimistic or very pessimistic about government actions, and only 17% are optimistic about the current government actions.
- Studies show that men are more optimistic about the effectiveness of government measures to improve businesses than women. Also, people who intend to be CEOs for less than three years are more pessimistic than those who intend to be CEOs for more than three years.
- 75% of CEOs believe that solving the country’s fundamental problems requires active partnership between the private and public sectors. According to a report by management consulting firm EY in 2024, the most optimal model for financing infrastructure development is a simultaneous partnership between the government and the private sector. However, the private sector always believes that it does not receive sufficient benefits and profits from partnerships with the government.
3. CEOs and personal issues
Leadership Motivation and Challenges:
- The results show that CEOs’ main motivations for remaining in their positions are a combination of internal and external factors.
- Among the intrinsic motivations, “enjoying the work process and personal interest in solving challenges and leading” had the highest response rate, at 66%, indicating that managers emphasize interest in the nature of their work. More than half of managers also chose a sense of commitment to personal values or the value of the organization’s mission.
- When discussing extrinsic motivations, nearly half of CEOs emphasized that financial issues were one of their top two motivations for staying in the position. Also, about 35 percent of managers cited meeting stakeholder expectations, which demonstrates the importance of managers’ responsibilities to shareholders, the board of directors, and other stakeholders.
- As a result of significant tests in this area, it was found that for companies with revenues of less than 20 billion Tomans, choosing financial income as a motivation to stay in the current position was significantly higher than for companies with a turnover of more than 20 billion Tomans.
- 57% of CEOs cited feeling overwhelmed and 51% cited uncertainty in the business environment as significant mental challenges.
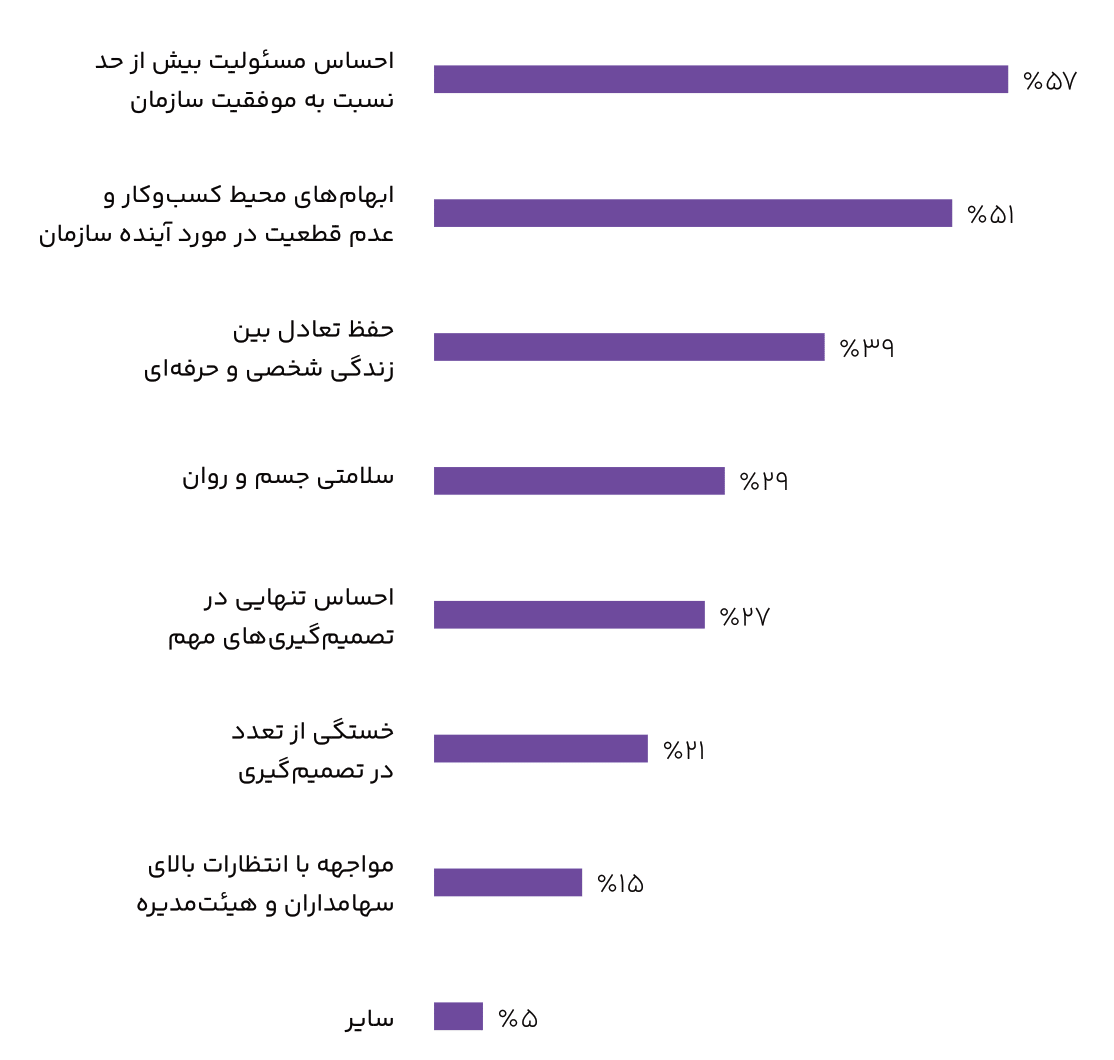
CEOs use a variety of methods to reduce stress, including spending time with family and friends (54%), exercise and physical activity (43%), pursuing personal interests (32%), and more.
4. CEOs and organizational issues
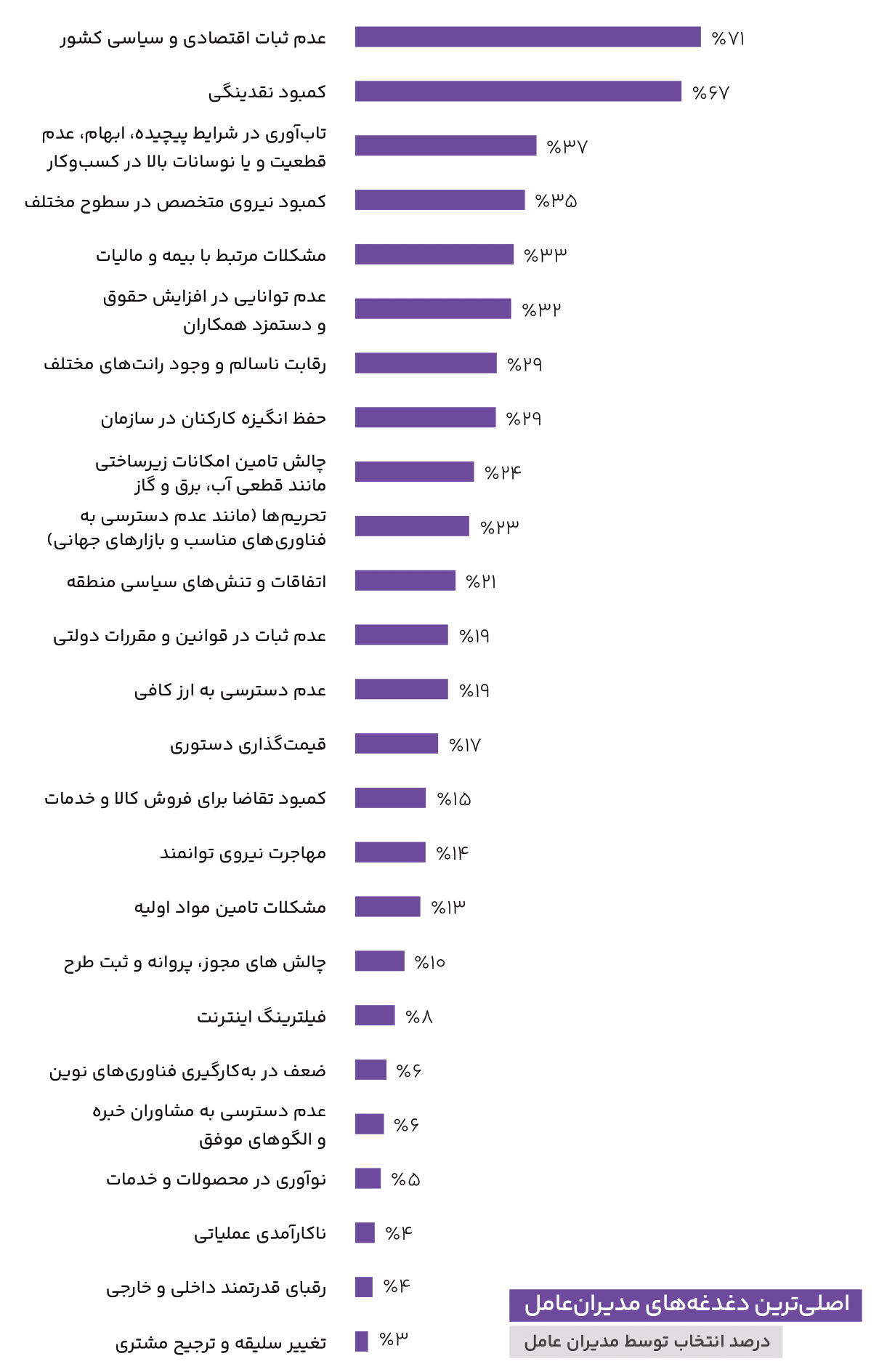
- After categorizing the concerns into three main groups: “Organizational and Business”, “Economy and Macro-Policy”, and “Market and Competitive”, it was observed that the percentage of selection in the “Market and Competitive” group was much lower than the other two, at around 17%. Hence, it can be said that most of the challenges selected by CEOs were in the “Organizational and Business” area (43%), followed by a small difference in the “Economy and Macro-Policy” area (40%).
- The most common concerns raised by CEOs for 1404 were “the country’s economic and political instability” and “lack of liquidity” (71 and 67 percent of CEOs chose these options, respectively). In third place, by a significant margin, is “resilience in complex and ambiguous situations,” which was mentioned by 37 percent of CEOs.
- Three of the selected concerns of managers have seen the greatest increase in importance compared to the results of last year’s report, indicating a significant increase in concern about these areas:
- Challenge of providing infrastructure facilities (11 levels increase)
- Regional political events and tensions (6 levels increase)
- Inability to increase the salary of colleagues (5 levels of increase)
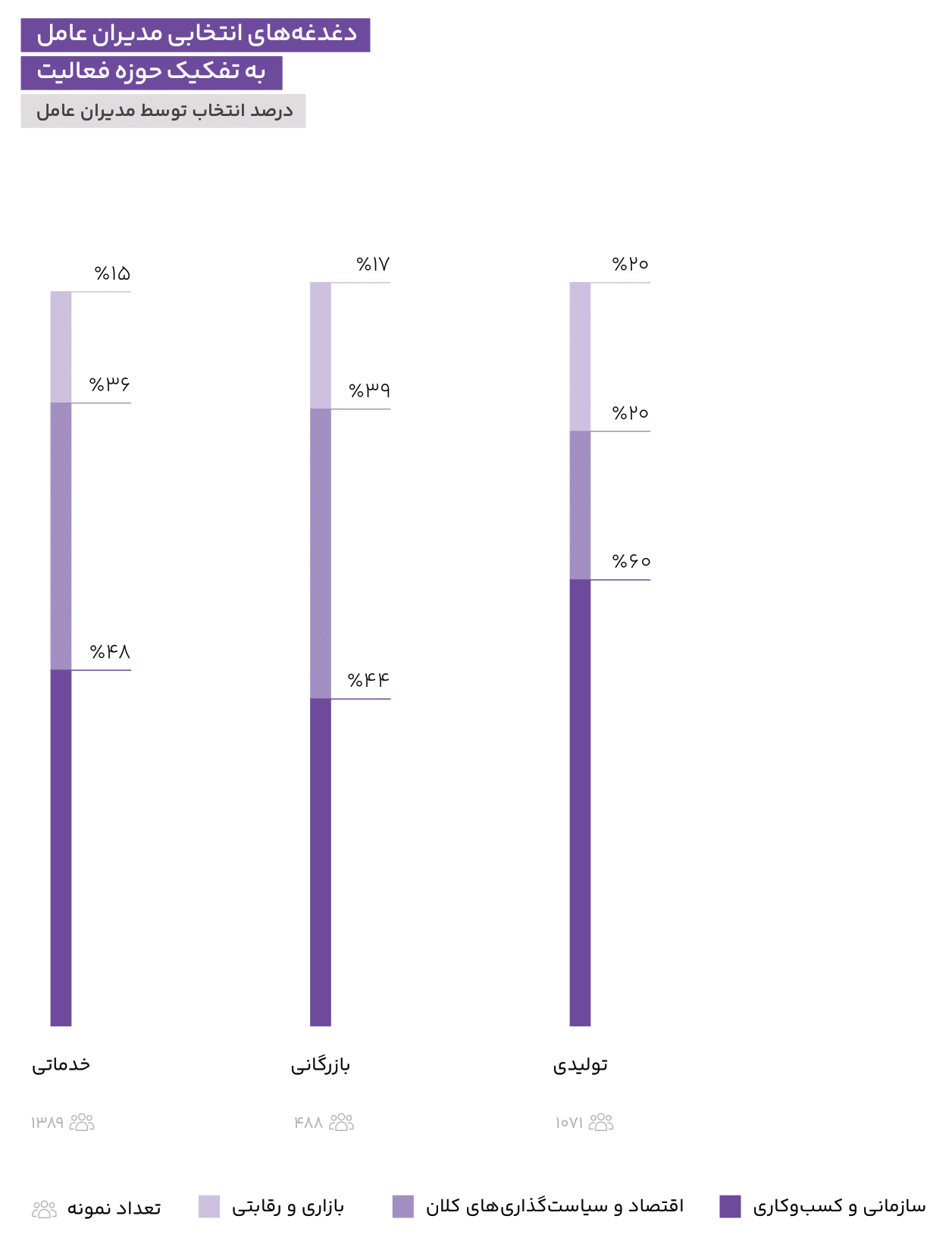
CEOs in the manufacturing sector have more “organizational and business” concerns and fewer “macroeconomics and policymaking” concerns than those in the commercial and service sectors.
Managerial focus and organizational changes:
- Reducing operating costs (35%) is one of the most important areas of focus for CEOs for 1404. A possible explanation for this is that CEOs are more likely to pursue contractionary policies in their businesses. Developing the domestic market and increasing product diversity are other areas of focus for CEOs in 1404, with 32 and 31 percent, respectively.
- In terms of professional development, CEOs prioritized financial management and investment, as they did last year. The strong presence of “digital transformation and artificial intelligence” and “industry-related technical and specialized knowledge” capabilities came in second and third place. On the other hand, the priority of international business development also declined compared to last year.
- The art of CEOs is to strike a balance between focusing on current and future issues. According to the survey, 66 percent of CEOs focus their attention on current and operational issues of the organization, and 17 percent stated that their main focus of thought and time was on issues related to business development and growth, and in other words, the future of the organization.
- The most dominant culture governing organizations, according to 59% of CEOs, is an organizational culture based on teamwork and human resource cooperation, and about 12% of managers admitted that no dominant aspect can be identified in their organizational culture.
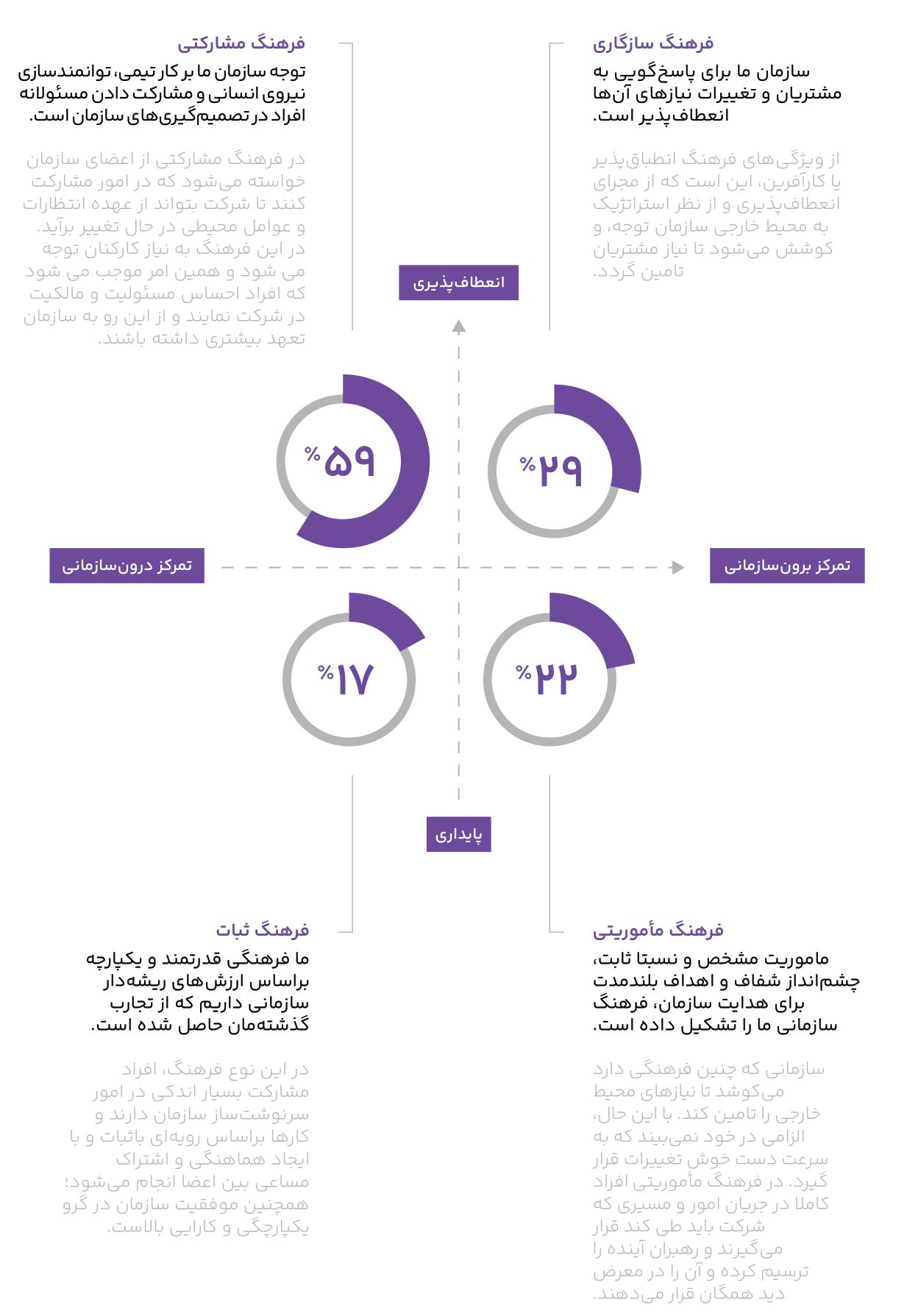
- Key people in companies with less than 10 years of experience have a clearer picture of their organization’s vision compared to companies with more than 10 years of experience.
- It can be said that in younger organizations, effective interaction with employees, especially key employees, and keeping them informed and involved in strategic issues has probably found its place and importance. Also, key people in companies with a manufacturing activity field have a significantly clearer and clearer picture of the organization’s vision than in other areas of activity, including services and commerce.
- Considering the results of the organizational culture section and the responses of CEOs who considered a participatory culture to be dominant in their organization, in contrast to the “low” and “very low” options selected in the question of clarity of vision by key individuals, a possible explanation is that the meaning of a participatory culture in an organization is participation in operational processes and not in its long-term and strategic planning.
The Artificial Intelligence Revolution and Technological Megatrends
More than half of CEOs have plans for the AI macro trend. About 30 percent of CEOs have no plans to use any of the macro trends.
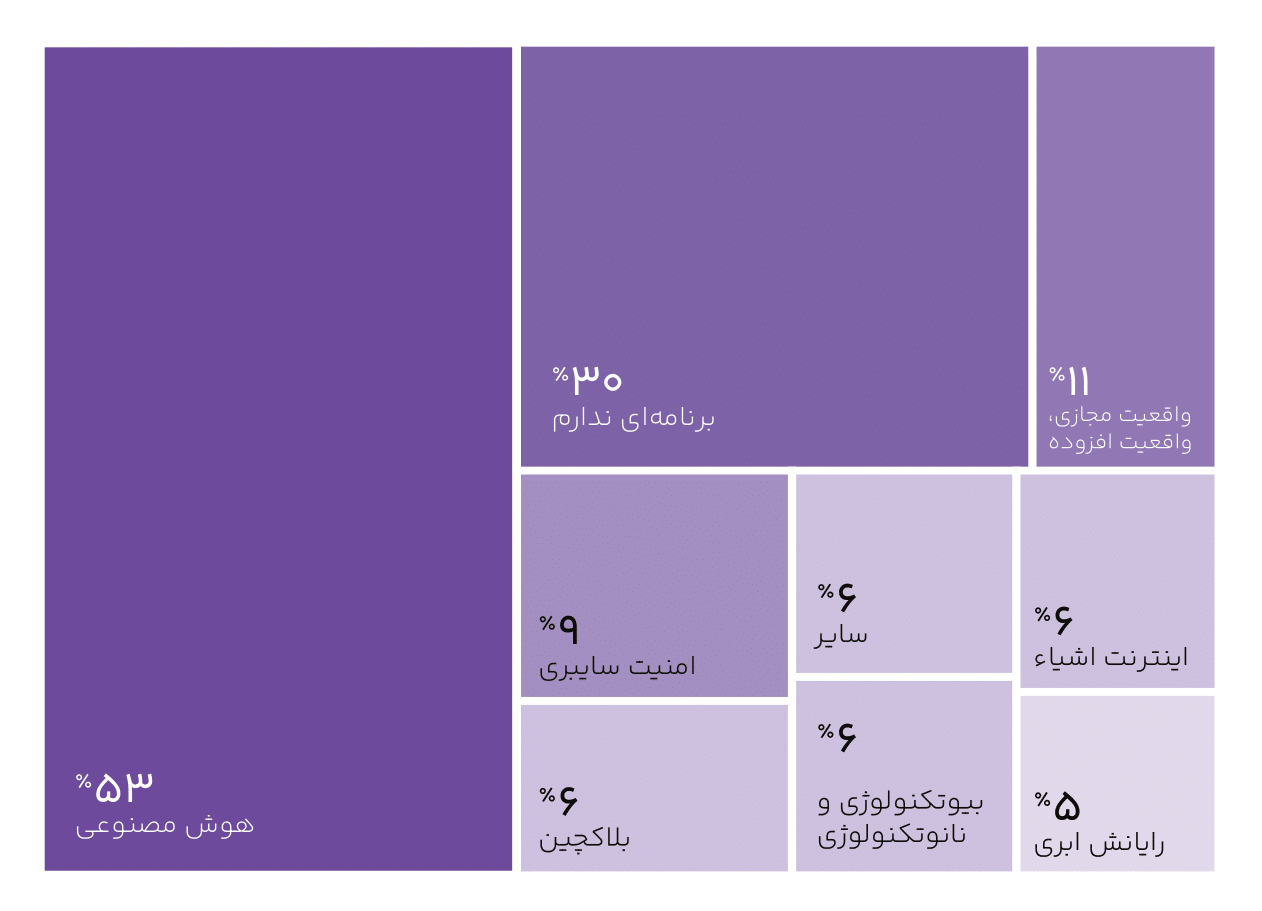
- Most CEOs prefer to use technological macro trends in the organization’s finance and research and development departments. The next priorities are human resources and marketing and sales departments.
- About 40% of managers have no plans to use AI in their organization. Also, 27% of managers are just getting acquainted with the concepts of AI. Managers active in the “Civil, Construction and Real Estate” and “Water and Waste Management” industries have the least plans to use this megatrend, while managers in the “Digital Economy” and “Information Technology” industries have the most plans to use this megatrend.
- According to the 2024 PwC report, despite the rapid global shift towards AI, it is important to note that AI-based technologies are still far from being fully mature and are far from being fully developed. Moving forward without a plan can increase organizational risks, so organizations need to strike a smart balance in their strategies. Leading organizations not only embrace AI, but also align their strategies with it.
The motivation for globalization
- About half of CEOs have stated that market development and increased sales are their goals for entering the international market. (47 percent of managers) After that, 44 percent of CEOs have chosen reducing the organization’s risk by entering new markets and foreign exchange earnings as their goals. 17 percent of participants do not have a specific goal for entering the international market.
- The key challenges that CEOs face when entering international markets are the complexity of the banking and financial system, chosen by 38%, and political relations with other countries, chosen by 35%.
5. CEOs and the liquidity issue
Operating costs and overcoming the liquidity problem
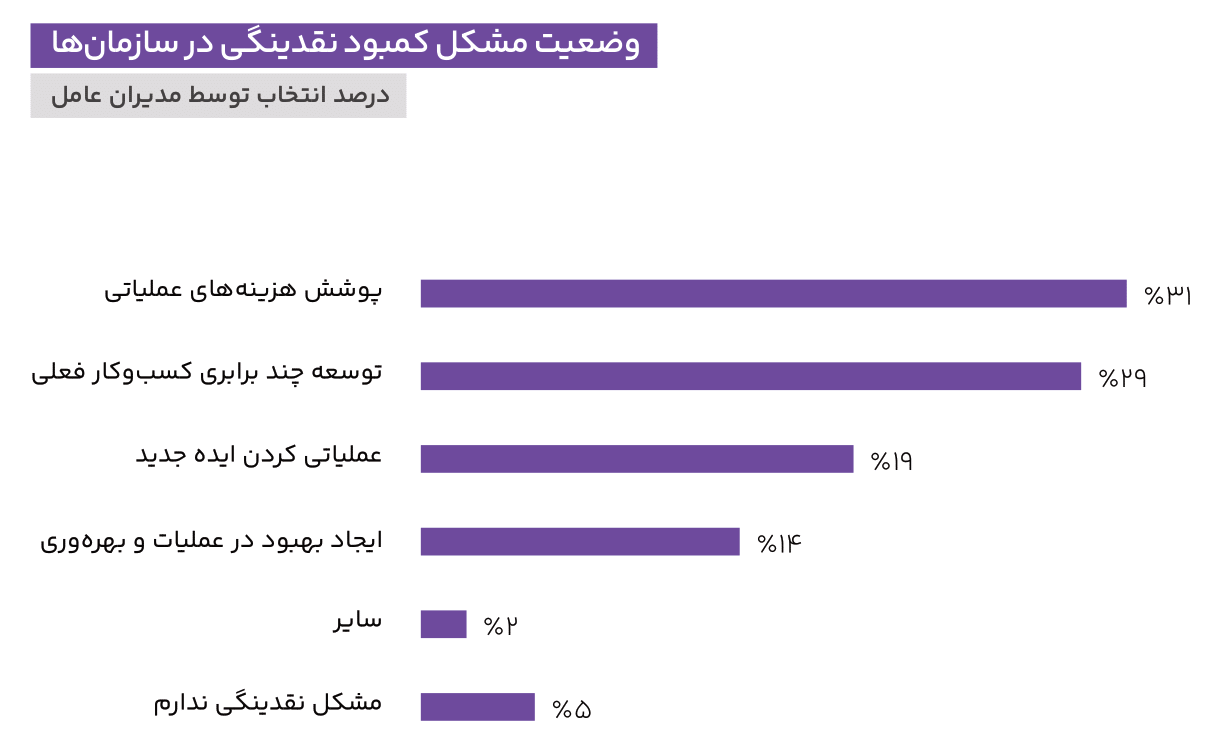
- CEOs adopt solutions to deal with this issue, depending on the nature of the liquidity problem and the capabilities of their organization; 44% of CEOs have chosen to take out a loan from the banking system and 43% have chosen to reduce operating costs as solutions to the liquidity problem.
- In the next choices, “attracting investors,” “making installment and credit purchases,” and “changing the pricing model of products and services or payment methods” were the most frequent solutions from CEOs. 4 percent of CEOs stated that they had no solution to overcome this problem.
- According to CEOs, the three main factors behind the liquidity crisis are economic recession, customer payment delays, and market shrinkage.
- From the perspective of managers, the two main measures of organizational success are revenue and net profit, which are selected by 50 and 42 percent of CEOs, respectively. In service companies, unlike the commercial and manufacturing sectors (which selected net profit/margin in the first place), the “revenue” indicator has taken the first place.
